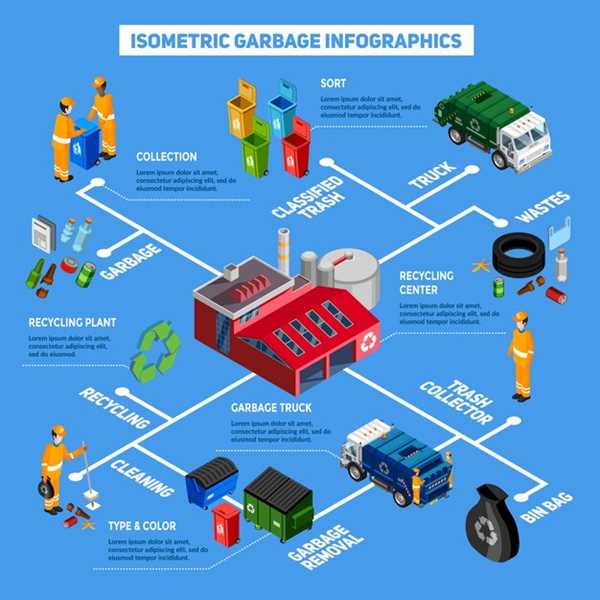
To initiate the transformation of an end-of-life automobile into reusable materials, commence with the proper assessment. Evaluate the vehicle’s condition and identify recyclable components, such as metals, plastics, and glass.
Next, disconnect the battery and drain all fluids, including oil and coolant, to prevent environmental contamination. This vital action safeguards both the environment and the health of workers involved in the subsequent phases.
Following the preliminary steps, the car should be dismantled. Remove valuable parts like catalytic converters and electronic components. Once extracted, these items can be sold or appropriately processed for repurposing.
After dismantling, the remaining shell must be crushed and shredded. This mechanical process facilitates the recovery of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. The resulting materials can enter the market for new products, closing the loop in resource management.
Finally, ensure that all hazardous materials are handled correctly, including batteries and fluids. This attention to detail is crucial for compliant and responsible disposal, benefiting both society and our planet.
Understanding the Initial Assessment and Preparation of Vehicles for Recycling
Conduct a thorough inspection of each auto to identify its components and materials. Check for hazardous substances like batteries, oils, and fluids that require special handling. Document the vehicle’s condition, including mileage and any damages, to determine its salvageable parts.
Remove valuable parts such as engines, transmissions, and electronics. This maximizes the potential for reuse and reduces waste. Ensure that components are separated into specific categories: metal, plastic, rubber, and glass. Utilize tools for efficient dismantling to minimize damage to recyclable materials.
Properly manage fluids by draining them into designated containers, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Label these containers clearly and store them safely to prevent leaks. This preparation phase is critical for maintaining safety and sustainability during the subsequent stages.
Once dismantled, verify and document the materials collected. Create a detailed inventory of reusable parts and materials, which can be valuable for resale or recycling purposes. This not only enhances efficiency but also promotes responsible auto management.
After completing assessments and preparations, sort the materials into the respective categories for processing. Collaborate with certified facilities to ensure that all materials are handled according to local and national standards. This careful handling supports environmental sustainability and resource conservation.
Detailed Breakdown of Components for Material Recovery and Reuse
Prioritize the extraction of metals, particularly steel and aluminum, which comprise the majority of an auto’s structure. Employ shredding technology to reduce vehicles into smaller pieces, making it easier to separate ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Next, focus on the plastics found in bumpers, dashboards, and interior components. These materials can be granulated and processed into pellets for reuse in manufacturing new products.
Don’t overlook the glass; windshields and windows can be crushed and recycled into various products, such as fiberglass or new automotive glass.
Another significant area involves fluids, including oil, coolant, and gasoline. Implement safe methods for draining and disposing of these substances to prevent environmental harm.
Lastly, prioritize tires, which can be repurposed into rubber mulch, asphalt, or even energy recovery through incineration. Follow local regulations for handling and transporting these materials to certified facilities.
Eco-friendly Disposal Methods and Legal Compliance in Auto Recycling
Utilize authorized facilities for the disposal of automotive components. These establishments follow environmental regulations and ensure safe handling of hazardous materials.
Implementing proper shredding techniques is essential. Shredders decrease the volume of scrap and separate recyclable elements from non-recyclable waste efficiently.
Ensure that fluid extraction occurs prior to dismantling. Oils, fuels, and other fluids must be removed to prevent contamination of soil and water sources.
Maintain compliance with local laws regarding waste management. Familiarize yourself with regulations that govern the disposal of parts like batteries, tires, and catalytic converters. Each material has specific requirements for environmentally responsible abandonment.
Engage with certified recyclers who possess the necessary permits. This guarantees adherence to both environmental laws and safety standards during the entire reprocessing phase.
Incorporate tracking systems for documentation of all materials processed. This provides transparency and verifies that disposal practices align with regulatory guidelines.
Prioritize reuse of parts when possible. Reselling or donating usable components minimizes waste and upholds sustainable practices.
Stay informed about local and national policies. Regular updates to recycling regulations may affect procedures and must be monitored consistently.


